In the manufacturing industry, plastic mold design is an essential process for creating products that meet quality and cost requirements. Plastic molds are used to shape plastic materials into the desired form, and designing them involves several key principles and considerations. In this article, we will explore these principles and considerations in detail.
Basic Principles of Plastic Mold Design
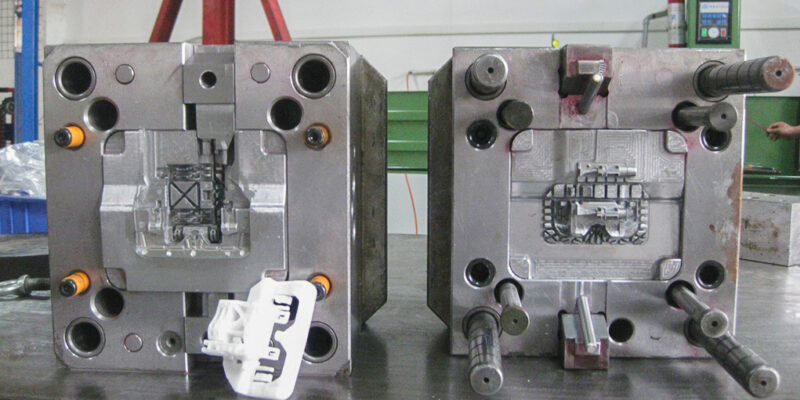
The design of a plastic mold is based on several key principles that ensure the production of high-quality parts. One of the most important principles is the parting line, which is the point where the two halves of the mold meet. The parting line should be carefully designed to ensure that the final product is of high quality and that it can be efficiently manufactured.
Another key principle of plastic mold making design is draft. Draft is the taper given to a vertical surface in a plastic part to make it easier to release from the mold. Without proper draft, the plastic part can become stuck in the mold, causing damage to the part or mold. Draft angles vary depending on the size and complexity of the part and the material being used.
Another critical principle is gate placement. Gates are the entry points where molten plastic material is injected into the mold. The gate must be placed in the optimal location to ensure that the material flows correctly throughout the mold, resulting in a high-quality part. The size and shape of the gate must also be carefully considered to ensure efficient and consistent filling of the mold.
Designing for Specific Materials
Designing a plastic mold also requires considering the specific properties of the plastic material being used. Different types of plastics have unique properties that affect the mold design process. For example, thermoplastics have a low melting point and can be molded repeatedly, while thermosetting plastics are harder and more brittle, making them less flexible during the molding process.
When designing a mold for a specific plastic material, the designer must take into account factors such as the material’s shrinkage rate, which affects the final dimensions of the molded parts, and the flow rate, which affects the mold’s filling and cooling time. Additionally, the designer must consider factors such as the type of plastic, its chemical properties, and its intended use.
CAD/CAM in Mold Design
In recent years, computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) have revolutionized the mold design process. CAD systems allow designers to create 3D models of molds quickly and easily, while CAM systems allow for precise manufacturing of molds using computer-controlled machinery.
The use of CAD/CAM systems has many advantages in the mold design process. It allows designers to create more complex molds that are not possible to make using traditional methods. Additionally, CAD/CAM systems allow for more precise and consistent manufacturing of molding products, resulting in higher-quality parts.
Designing for Production Volume
The production volume is another critical consideration when designing a plastic mold.
Low-volume production molds have different design requirements than high-volume production molds. For low-volume production, a simpler mold design may be sufficient, while high-volume production molds require more complex designs to ensure consistent and efficient manufacturing.
Designers must also consider the material being used when designing a mold for high-volume production. Some plastics, such as polycarbonate, can wear down the mold more quickly than others, requiring more frequent maintenance and replacement.
Designing for Complex Parts
Designing molds for complex plastic parts requires additional considerations. For example, parts with undercuts or thin walls require more complex mold designs to ensure that the final product is of high quality and can be efficiently manufactured.
Undercuts are areas of a part that prevent it from being easily ejected from the mold, requiring additional mold components or mechanisms to release the part.
Thin walls are also a complex challenge in mold design. The wall thickness must be consistent to ensure that the part is of high quality and that it can be manufactured efficiently. Additionally, the mold must be designed to withstand the high pressure and temperature of the molten plastic material, which can cause warping or other defects in the final product.
Design Validation and Testing
Before production, it is essential to validate and test the mold design to ensure that it is suitable for manufacturing high-quality parts. Validation and testing can be done through computer simulations or physical testing of the mold and the final product.
Computer simulations can identify potential issues in the mold design, such as improper gate placement or inadequate cooling. Physical testing can reveal issues that are not apparent in simulations, such as the presence of injection molding defects or the inability to release the part from the mold.
Conclusion
Designing a plastic mold is a complex process that requires careful consideration of many factors. The principles of parting line, draft, and gate placement must be considered to ensure a high-quality product. The type of plastic material being used and its specific properties must also be considered, along with the production volume and the complexity of the part being molded.
CAD/CAM systems have revolutionized the mold design process, allowing for more complex designs and more precise manufacturing. Finally, validation and testing of the mold design are essential to ensure a high-quality final product.
Designing plastic molds is a challenging but essential process in the manufacturing industry. By understanding the principles and considerations outlined in this article, designers can create molds that produce high-quality parts efficiently and cost-effectively.









Comments