Introduction
Solenoid valves play a crucial role in fluid control systems, as they enable precise and reliable control of the flow of liquids and gases. These electromechanical devices have become indispensable in a wide range of industries due to their efficiency and versatility. This article aims to provide an understanding of the working principle of solenoid valves, various types, factors to consider when selecting one, and the applications where they are most commonly used.
Basic Working Principle of Solenoid Valves
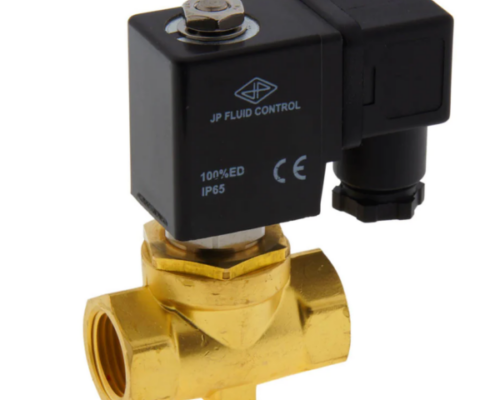
A solenoid valve consists of two main components: the solenoid (a coil of wire) and the valve body. The solenoid is an electromagnetic device that generates a magnetic field when an electric current is applied to it. This magnetic field opens or closes the valve by controlling a movable plunger within the valve body, allowing or stopping the flow of fluid.
Types of Solenoid Valves
There are three primary types of solenoid valves, each with its specific operating principle and application suitability:
- Direct-acting solenoid valves: These valves have a plunger directly connected to the valve’s orifice. When the solenoid is energized, the plunger moves and opens or closes the orifice. Direct-acting solenoid valves are suitable for low-pressure applications and can operate with zero differential pressure.
- Indirect-acting (pilot-operated) solenoid valves: In these valves, the solenoid operates a smaller pilot valve, which controls the main valve. The pressure differential across the valve causes the main valve to open or close. Indirect-acting solenoid valves are suitable for high-pressure applications but require a minimum pressure differential to operate.
- Semi-direct-acting solenoid valves: These valves combine features of both direct-acting and indirect-acting solenoid valves. Semi-direct-acting valves can handle higher pressures than direct-acting valves, and they can operate with low or no differential pressure.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Solenoid Valve
To choose the right solenoid valve for a specific application, it is essential to consider several factors:
- Media type and compatibility: The solenoid valve material should be compatible with the fluid being controlled to avoid corrosion and ensure proper sealing.
- Pressure and flow requirements: The solenoid valve should be able to handle the system’s pressure and flow requirements without causing significant pressure drops.
- Valve size and port connections: The valve’s size and port connections should match the system’s pipe size to ensure proper installation and flow control.
- Voltage, power, and duty cycle: The solenoid valve should be compatible with the available power supply and designed for the required duty cycle to ensure reliable operation.
- Environmental conditions: Consider the temperature and humidity levels in the operating environment, as extreme conditions may affect the performance and lifespan of the solenoid valve.
- Response time and safety factors: Evaluate the desired response time of the valve and any safety factors, such as fail-safe or explosion-proof requirements, that may apply to your specific application.
When to Use a Solenoid Valve
Solenoid valves are commonly used in various industries and applications, including:
- Water and wastewater treatment: In these systems, solenoid valves control the flow of water, chemicals, and other fluids required for treatment processes. For example, they can be used to dose specific chemicals for pH control or to manage fluid distribution in filtering processes.
- Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems: Solenoid valves regulate the flow of refrigerant, hot water, and steam in HVAC systems, ensuring optimal temperature and humidity control. They can be found in various components, such as boilers, chillers, and air handling units.
- Industrial automation and process control: Solenoid valves play a vital role in automating manufacturing processes, controlling the flow of fluids in various production stages. For instance, they are used in food and beverage processing to manage the flow of ingredients or in pharmaceutical production for precise dosing of chemicals.
- Irrigation and agricultural applications: These valves help manage water distribution in irrigation systems and control the flow of fertilizers and other agricultural chemicals. Automated irrigation systems using solenoid valves can achieve optimal water usage and reduce waste by controlling the flow based on factors like soil moisture levels and weather conditions.
- Fuel and gas control in vehicles and equipment: Solenoid valves are used to regulate the flow of fuel and gas in engines, ensuring efficient combustion and emission control. They can be found in fuel injection systems, emission control systems, and natural gas delivery systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Solenoid Valves
Solenoid valves offer several benefits and some drawbacks:
Pros:
- Fast response times: Solenoid valves can open and close rapidly, providing precise fluid control.
- High reliability: These valves have few moving parts, resulting in low maintenance and long service life.
- Compact and lightweight design: Solenoid valves are small and lightweight, making them suitable for space-constrained applications.
Cons:
- Limited to on-off control: Solenoid valves are primarily used for on-off flow control, with limited capabilities for proportional control.
- Potential for electromagnetic interference: Electromagnetic fields generated by solenoid valves can cause interference with nearby electronic devices if not adequately shielded.
- Electrical Power Dependency: Solenoid valves require a continuous electrical power supply to operate. In the event of a power outage or electrical failure, solenoid valves may become non-functional and unable to control the flow.
- Sensitivity to Contaminants: Solenoid valves can be sensitive to contaminants or debris present in the fluid or gas being controlled. Particles or impurities can potentially interfere with the proper operation of the valve, leading to reduced performance, leakage, or blockage.
- Cost and ease of installation and maintenance: Solenoid valves can vary in cost, and more complex systems may require additional installation and maintenance efforts. Balancing cost and complexity with the required level of control is crucial when selecting solenoid valves.
Conclusion
Selecting the right solenoid valve for a specific application is crucial to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Understanding the working principles, types, selection factors, and common uses of solenoid valves helps users make informed decisions when integrating these essential devices into their fluid control systems. Considering factors such as compatibility, pressure and flow requirements, environmental conditions, response time, and available resources are vital to make the best choice for a given application.









Comments